Nicole Drakos
Research Blog
Welcome to my Research Blog.
This is mostly meant to document what I am working on for myself, and to communicate with my colleagues. It is likely filled with errors!
This project is maintained by ndrakos
MIRISim Scene Part II
To make simulated images of the Miri observations, I am using MIRISim, as outlined here.
One component needed to make these observations is a “scene”, which you can either create in MIRISim from a list of objects, or can input as a FITS file. As detailed in this previous post, I was having trouble creating a scene using the first method (there seemed to be memory issues). Therefore I decided to create a FITS file with all the sources, and input this. Vasily kindly shared his code with me, and I have altered it to create a scene, which I’ll detail in this post.
Creating an empty FITS File
Here is my code to create the scene. Right now it has no sources, and is just all zeros
######################
# Function
######################
def create_hdul(bounds, pixscale, rota=0):
# Creates an hdul with RA and Dec between the specified bounds. Data is all zeros.
# bounds: [RAmin, RAmax, Decmin, Decmax], degrees
# pixscale: degrees/pixel
# mydata: array to store
ra_length = int( (bounds[1]-bounds[0])/pixscale) #In pixels
dec_length = int((bounds[3]-bounds[2])/pixscale) #In pixels
crval = [bounds[1]-(bounds[1]-bounds[0])/2,bounds[3]-(bounds[3]-bounds[2])/2] #centre
crpix = np.array([ [0,ra_length/2,ra_length-1] , [0,dec_length/2,dec_length-1] ])
world_coord = SkyCoord(ra=[bounds[1],crval[0],bounds[0]],dec=[bounds[2],crval[1],bounds[3]],frame='fk5', unit='deg')
w = fit_wcs_from_points(xy = crpix, world_coords = world_coord,projection="TAN")
#Make hdul
myhdul = fits.HDUList()
myhdul.append(fits.ImageHDU())
#Add header
myhdul[0].header.update(w.to_header())
myhdul[0].header['PC1_1']=-np.cos(rota)
myhdul[0].header['PC1_2']=np.sin(rota)
myhdul[0].header['PC2_1']=np.sin(rota)
myhdul[0].header['PC2_2']=np.cos(rota)#(bounds[3]-bounds[2])/dec_length #.11/3600
myhdul[0].header['CDELT1'] = (bounds[1]-bounds[0])/ra_length
myhdul[0].header['CDELT2'] = (bounds[3]-bounds[2])/dec_length
#Add data
myhdul[0].data = np.zeros((ra_length,dec_length)).T
return myhdul
##########################################
# Create Empty Image
#########################################
print('Set-up')
sources_hdul = create_hdul(bounds, pixscale/3600)
#sources_hdul.writeto('testblank.fits', overwrite=True)
Generating Each Galaxy (Stamp)
I can generate a stamp of each galaxy using make_model_sources_image from photutils and inputting a Sersic model (models.Sersic2D() from astropy).
I also need to specify a stamp size. I did a stampsize of:
stamp_size = int(np.ceil(radius[i]*5)*oversample) #pixels
stamp_size = max(stamp_size,5)
This should go out to 5 times the half light radius, and have oversample=10 pixels per arcsecond.
Sersic Parameters
This function takes in the normal Sersic parameters (effective half-light radius, sersic index, ellipticity, position angle and amplitude). These are all included in the DREaM catalog, but most need to be converted.
A special note on the amplitude. I have the flux within the MIRI band, but the code takes in the surface brightness at the half-light radius.
To calculate this, I use the fact that the total luminosity in a sersic profile is given by:
\[L = I_e R_e^2 2 \pi n \dfrac{e^{b_n}}{b_n^{2n}} \Gamma (2n)\]where \(I_e\) is the intensity at the effective radius $R_e$ that enclses half the total light from the model (see these notes).
and then solve for the surface brightness at \(R_e\) by dividing the total flux by \(R_e^2 2 \pi n \dfrac{e^{b_n}}{b_n^{2n}} \Gamma (2n)\).
Adding Stamp to Full Image
Now that I have the machinery in place to make stamps of each galaxy, I add them to the scene as follows.
1) Create an HDUList from Stamp
First, I give a wcs to the stamp, and store it as an HDUList.
#Make hdul
myra = ra_list[i]; mydec = dec_list[i]
size_arcsec = stamp_size/oversample # size of stamp in arcsec
mybounds = [myra - size_arcsec/3600/2, myra+ size_arcsec/3600/2, mydec-size_arcsec/3600/2, mydec+size_arcsec/3600/2]
stamp_hdul = create_hdul(mybounds, size_arcsec/stamp_size/3600 )
stamp_hdul[0].data = sersic_stamp.T
stamp_hdul.writeto('teststamp.fits', overwrite=True)
2) Get cut-out of big image
The goal is to map the stamp to the big image. However this is really slow to do on the full image, so instead I use a cutout of the big image. This cutout can be obtained by the function “Coutout2D”. I take the size to be 1.1 times the size of the stamp, just in case there is some pixel rounding error (it would probably be fine really, but this doesn’t slow things down much).
Here is my code for cutting out the desired region “cut_im”, and then creating an HDUList of it.
#Get cut-out
cut_im = Cutout2D(sources_hdul[0].data,wcs=WCS((sources_hdul[0].header)),position=pos,size=(1.1*size_arcsec/3600*u.deg),mode="trim",copy=False)
cut_hdul = create_hdul(bounds, pixscale)
cut_hdul[0].header.update(cut_im.wcs.to_header())
cut_hdul[0].data = cut_im.data
3) Add the stamp to the cutout
Now that I have my cutout region, I want to map the stamp to this cutout.
#Add stamp to cutout
cut_data, footprint = mosaicking.reproject_and_coadd([cut_hdul[0],stamp_hdul[0]],cut_hdul[0].header,reproject_function=reproject_interp,combine_function='sum')
cut_hdul[0].data = cut_data; cut_hdul.writeto('testcut.fits', overwrite=True)
Now this cutout region should have the galaxy added to it, and be in the same WCS as the big scene image!
Example:

This is one galaxy with the stamp on the left, and the cutout on the right. I matched the WCS on these two images in DS9 (Frame > Lock > Frame < WCS), so you can see the cutout is slightly bigger.
4) Store Information
Finally, I want to store this cut-out in my total data:
xmin = cut_im.ymin_original; xmax = cut_im.ymax_original+1
ymin = cut_im.xmin_original; ymax = cut_im.xmax_original+1
sources_hdul[0].data[xmin:xmax,ymin:ymax]=cut_data
Full Code
Basically I loop through all the galaxies and add them each to the full image.
Here is my full code:
And here is what the data looks like
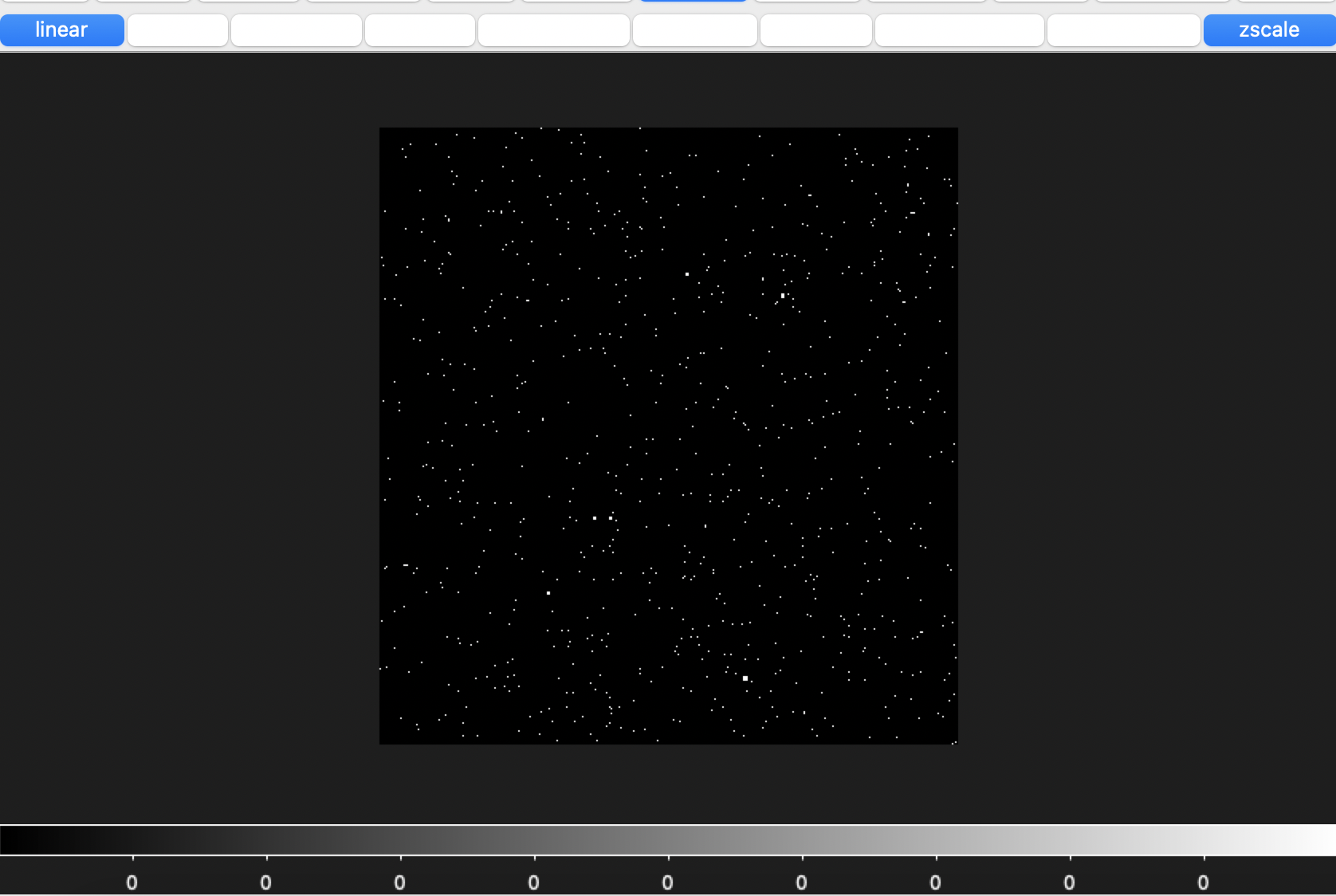
The galaxies look distributed right, but they appear very small. This is possibly just an issue with how I am displaying the data, but I suspect something is wrong with the units.
Next Steps
1. Check Galaxies Okay
I need to double check the positions are correct (at first glance this is okay).
I also want to visually inspect the sizes, fluxes, ect. and see why it looks a little strange
2. Add Full Catalog
Right now I just have my test catalog in this scene. I need to add the fainter galaxies too. If this is too slow to do on my laptop, it should be quite easy to parallelize: I can just run this code for a subset of galaxies, and then add all the data together.
3. Background and Stars
The current plan is to include the Background and Stars using MIRISim’s functionality. But I may decide to add them directly to this image later. Note that including stars will require a bit of work to determine their brightness in the F770W band.
4. Run in MiriSim
I already tested I have MiriSim working for FITS images (using Jed’s example). I need to run this on my scene (at a fixed pointing), and then pass it along to e.g. Santosh, Daizhong, and make sure we have things working for the pipeline (and iterate over any problems in my simulation!)
5. Specify Pointing/Dither Properly
As detailed in the previous post, inputting a pointing and dither pattern might not be the most straight-forward in MIRISim. Daizhong has done a bit of work looking into this, so I can hopefully see what he’s done and adjust the code accordingly.